Lenovo pc BIOS. How to enable TPM and Secure Boot in BIOS for Windows 11
How to Enable Virtualization (VT) on Windows 10/11
As we know, the operating system of the Android emulator is different from the Windows operating system. While by enabling virtualization technology, you can play mobile gamesapps on your Windows 10 or 11. In this article, you can get the ultimate steps to enable virtualization technology and the problems you may meet during the process.
Quick Navigation
Check this video out if you want to learn quickly how to enable Virtualization (VT) on your PC.
Why do I have to enable virtualization on Windows 10/11
The emulator needs to run in an independent environment separating from the Windows OS, and VT is designed for providing this environment. Enabling virtualization allows the emulator to get more computer resources to run apps or games. In order to ensure the smoothness of gaming experience on LDPlayer, virtualization must be enabled.
Enabling VT will not cause any harm to the computer. Sometimes you can’t even launch LDPlayer when it is disabled. On the contrary, after VT is enabled, the emulator runs 10 times faster! No more FPS lag/stutter in various games.
First check whether virtualization is supported by your PC
However, some PCs don’t support virtualization. Now the question is, how do I know if virtualization is supported by my PC?
Step 1: Click the following link to download a portable tool, which can be used to judge whether VT is supported or enabled. leomoon.com/static/?file=leomoon-cpu-v_win.zip
Step 2: Directly double-click this file with an extension of.exe after it is downloaded.
Step 3: You will get one of the following three results.
As you can see the pictures above, the first picture shows that virtualization is not supported and so can’t be enabled. The second one shows that your PC supports virtualization but you have disabled it. If you are in the situation of the last picture, you can close this guide and enjoy your happy gaming on LDPlayer.
Second check whether virtualization is enabled
Y ou can also check whether virtualization is enabled in the following way.
See if the character ‘VT’ is shown in the top right corner of LDPlayer. If it is, VT is disabled or used by other computer programs. If it isn’t, VT is enabled and so you can directly ignore this tutorial.
Steps to enable VT on Windows 10 or 11
Please note that you have to do all these steps of enabling virtualization by yourself because you will enter BIOS and Windows operating system won’t run on your computer at that time. That is to say, we can’t give you a hand through TeamViewer which only runs on Windows operating system.
Step 1: Enter BIOS after re-boots your PC
Restart your computer, and p ress the F2 or Del key repeatedly as soon as your computer shuts down.
If you still can’t enter BIOS after doing that, please try pressing another key. Now you may want to know which key you should press. Each brand of laptop, desktop and motherboard have different BIOS entry keys. Please view the table below to find your own laptop, desktop or motherboard. If you can’t find yours, please search Google for an accurate answer applying to your own brand of laptop, desktop or motherboard.
Step 2: Enable Virtualization Technology in your BIOS settings
After you enter BIOS, press the ←, →, or key to switch from one item to another if you don’t see your cursor on your screen. In addition, pressing the Enter key will allow you to have one item selected.
Find the VT item which is usually named Intel(R) Virtualization Technology, Virtualization, Virtual, VT-X or SVM. In general, you can find it here: Advanced Processor Configuration/Security.
Select Intel(R) Virtualization Technology and change to Enabled.
Last but not least, press the F10 key to save and exit
Extra: Guides to enable VT on different computers or motherboards
PC boots too fast to access BIOS?
The computer’s startup speed is too fast, which makes it too late to press the corresponding key to enter the BIOS. You can refer to this guide and follow the operations to solve the fast startup problem in the computer.
VT has been enabled in BIOS, but not detected by LDPlayer?
The virtualization has been enabled on Windows 10/11, but the VT prompt still appears in the upper right corner of the emulator. This may be caused by the Hyper-V of your Windows operating system or the antivirus program Avast occupying the computer VT technology. Check this tutorial to solve the VT not detected by LDPlayer error.
Other optimization tutorials for Android Emulator
If you still feel that the emulator lags after enabling the virtualization technology, you can read the following emulator optimization tutorials.
Thank you for using LDPlayer, and we hope you will like it. If you have other questions, you can contact us through the following Email: support@ldplayer.net
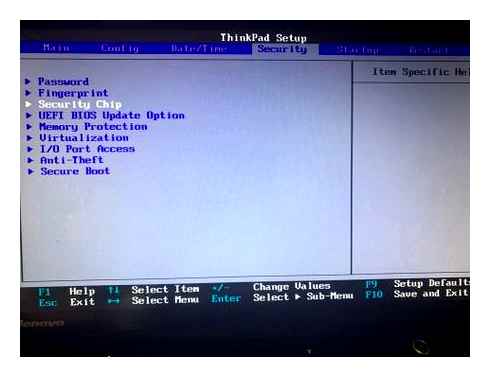
How to enable TPM and Secure Boot in BIOS for Windows 11
Windows 11 requires TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot enabled to install, and here are the steps to enable the security features on your computer.
If you plan to upgrade to Windows 11, you must first check and enable TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot in the BIOS (UEFI) of your computer’s motherboard (from Asus, Dell, MSI, GigaByte, etc.) as part of the preparation.
On Windows 11, one of the most significant changes is the requirement for Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0 and Secure Boot. According to Microsoft, TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot are needed to provide a better security environment and prevent (or at least minimize) sophisticated attacks, common malware, ransomware, and other threats.
TPM is a piece of hardware, usually (but not always) integrated into the motherboard, which offers a secure environment to store and protect the encryption keys when encrypting the hard drive using features like BitLocker. On the other hand, Secure Boot is a module that ensures that the device boots only using the software that the manufacturer trusts.
This guide will teach you the steps to check and enable TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot to install Windows 11. (See also the steps to enable these two security features on VMware Workstation and Hyper-V to run the new OS on a virtual machine.)
Check if TPM 2.0 is present for Windows 11
To determine if TPM is enabled for Windows 11, use these steps:
If the computer includes a TPM chip, you’ll see the hardware information and its status. Otherwise, if it reads “Compatible TPM cannot be found,” the chip is disabled on the UEFI, or the device doesn’t have a compatible Trusted Platform Module.
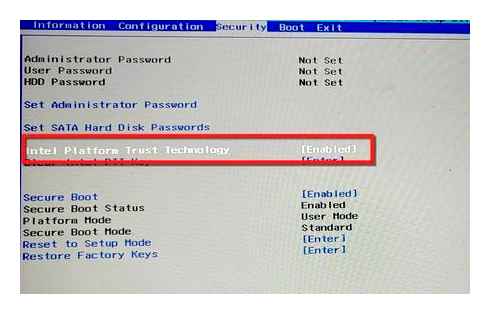
Enable TPM 2.0 in BIOS for Windows 11
To enable TPM 2.0 in the BIOS to fix the Windows 11 installation, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Update Security.
- Click on Recovery.
- Under the “Advanced startup” section, click the Restart now button.
- Click on Troubleshoot.
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click the “UEFI Firmware settings” option.
- Click the Restart button.
- Click the advanced, security, or boot settings page, depending on the motherboard.
- Select the TPM 2.0 option and choose the Enabled option.
If the motherboard doesn’t have a TPM chip and you are running an AMD processor, the module it’s may be built into the processor, and the option will appear as “fTPM” (firmware-based TPM 2.0) or “AMD fTPM switch.” If the device is an Intel-based system, TPM 2.0 will be available as Platform Trust Technology (PTT).
If the computer does not have a TPM option and this is a custom build, you may be able to purchase a module to add the support. However, you want to consult the motherboard’s manufacturer’s website to confirm that the support exists.
After you complete the steps, the Windows 11 check should pass, allowing you to upgrade the computer to the new OS.
Check if Secure Boot is present for Windows 11
To determine whether Secure Boot is enabled on the computer, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for System Information and click the top result to open the app.
- Click on System Summary on the left pane.
- Check the “Secure Boot State” information and confirm the feature is turned “On.” (If not, you need to enable the option manually.)
Once you complete the steps, you can continue with the Windows 11 installation if the security feature is enabled. Otherwise, you must follow the steps to enable it inside the UEFI firmware.
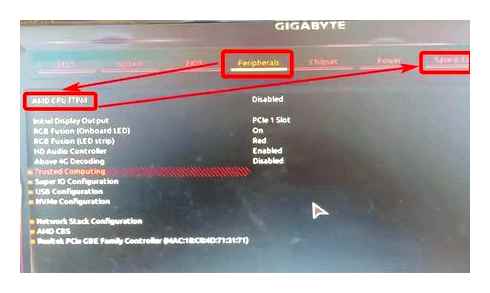
Enable Secure Boot in BIOS for Windows 11
If your computer uses the legacy BIOS, you first need to convert the MBR drive to GPT, switch to UEFI mode, and enable Secure Boot. Otherwise, the computer will no longer boot if you enable the newer firmware. If you are trying to perform a clean installation, you can skip the conversion, but this is a requirement if you are trying to upgrade from the Windows 10 desktop.
To enable Secure Boot in the BIOS firmware, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Update Security.
- Click on Recovery.
- Under the “Advanced startup” section, click the Restart now button.
- Click on Troubleshoot.
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click the “UEFI Firmware settings” option.
- Click the Restart button.
- Click the advanced, security, or boot settings page, depending on the motherboard.
- Select the “Secure Boot” option and choose the Enabled option.
Almost every device with UEFI firmware will include Secure Boot, but if this is not the case, you will need to upgrade the system or consider getting a new computer that meets the Windows 11 requirements.
After you complete the steps, the computer should pass the hardware verification process to proceed with the in-place upgrade or clean install of Windows 11.
We may earn commission for purchases using our links to help keep offering the free content. Privacy policy info.
All content on this site is provided with no warranties, express or implied. Use any information at your own risk. Always backup of your device and files before making any changes. Privacy policy info.
Since you are here.
I’ve got a small favor to ask. This is an independent site, and producing content takes a lot of hard work. Although more people are reading Pureinfotech, many use adblocker. Thus advertising revenue is falling fast. And unlike many other sites, there is no paywall blocking readers here. So you can see why your help is needed. If everyone who finds this website useful and helps to support it, the future would be much more secure. Thank you.
If you use adblocker, please disable it for this site.
125 raised so far by 11 people.
How to Safely Overclock Your CPU for PCs Laptops
If you want to improve your computer’s performance without spending money on an expensive upgrade, overclocking your CPU is a great way to make your PC run faster. Learn how to push your processor to its limit, check your computer’s temperature, and achieve a stable overclock. Then, keep your CPU optimized with dedicated optimization software.
When overclocking your CPU, you’re trying to unlock maximum performance while preventing damage to your hardware. So, you’ll need to keep a close eye on your system and make sure your computer doesn’t begin to malfunction.
Keep reading for our step-by-step guide on how to safely overclock your CPU. Then find out exactly what overclocking does, if your machine actually can be overclocked, and how to overclock Intel CPUs.
Step 1: Determine your CPU’s core temperature
Before getting started, you need to check your CPU’s temperature, because overclocking will increase it — and you’ll want to measure the temperature change. You can check CPU temps in BIOS or with a third-party too.
If your machine’s already running hot, fix the overheating problem before proceeding.
Step 2: Perform a system stress test
If you want to perform a serious CPU overclock, you should look at stress testing the CPU for a few hours. You want to know that your current system is stable under the current default clock speed. And if you encounter problems later, you’ll want to know why.
A useful tool for this use is Prime95, which puts a constant 100% load on all CPU cores. Let it run for one or two hours and see what happens, while keeping a close eye on temperatures throughout (see the step above).
Use a program like Prime95 to stress test your CPU before overclocking.
Step 3: Check your CPU’s performance
To measure improvements, you need to know where you’re starting from. Begin by benchmarking your current CPU performance, using a tool like Cinebench, which simulates a rendering workload. Extract the archive and fire up Cinebench Windows 64 Bit.
After launching Cinebench, click the Run button next to the CPU listing in the left panel. After the rendering is complete, you’ll see the current score. Write that number down so you can refer to it later if you want to compare scores.
Another benchmarking tool I like is 3DMark Basic, which focuses on gaming performance. If you use this benchmarking tool, remember to monitor your CPU’s temperature to learn how hot it gets under this load.
Before overclocking, make sure your PC’s current setup is dialed in. Avast Cleanup will automatically get rid of resource-draining apps to make sure your computer is running as smooth and fast as possible. That way, when you go to overclock, you’ll know that you’re starting from an optimal base.
Step 4: Access your BIOS
The only reliable way to overclock your system is to change the settings in your computer’s BIOS. The BIOS (sometimes referred to as UEFI) contains your PC’s key settings.
Ready to get started? To access the BIOS, you need to turn your computer off and turn it back on. As the computer restarts, press the DELETE, F2, or F10 key repeatedly. Doing so lets you enter your PC’s BIOS controls. The exact key combination varies by manufacturer brand and model. Usually, a message is displayed — for example, “Press F2 to enter Setup.”
Your BIOS likely looks different from the ones in these screenshots, but you should see some text like, Advanced CPU Core Settings or OC/Overclocking. This is where you’ll find the settings to overclock the CPU.
Step 5: Choose between automatic and manual overclocking
Depending on the motherboard manufacturer, the BIOS may provide an Automatic Overclocking or OC Level function. These options give you a bit of an overclocking boost at safe levels, but the results are usually nothing special. That’s why we recommend going with the manual approach outlined in the next step.
Step 6: Adjust the CPU multiplier
The first step to increase the clock speed should be to increase the multiplier. This uses the base clock built into the motherboard (usually 100 MHz) — multiplying that number yields your clock speed. For example, a multiplier of 36 (x100 MHz) gets you 3.6 GHz.
Gradually raise the multiplier one step at a time. You can usually do this by typing in the number or using the key on the keyboard. Proceed slowly and treat this as an iterative process. Speed up your computer a little bit. If all goes well, go back and dial it up some more.
Start by increasing the multiplier for one core and go slowly for the others. The more cores you overclock, the hotter (and more unstable) your system will become.
Save your settings and reboot the system. Then, stress test and benchmark to measure your CPU’s stability and performance.
It’s important to note that overclocking the multiplier only gets you so far (in our case from 36 to 39) before your computer becomes unstable. That’s because your CPU requires a bit more juice to get going.
To give your CPU more power, find the CPU voltage setting. In your BIOS controls, this may be called CPU VCCIN, CPU Vcore, Dynamic Vcore, or simply CPU Voltage. It’s usually set to 1.25 or Auto by default. Increase this value slowly, for example to 1.4 or 1.5. This gives you a bit more room for overclocking, which means you can try increasing the multipliers a bit more.
By increasing voltage and multipliers one by one, you’ll eventually find the maximum overclock on your system. But every time you overclock a CPU, your computer runs hotter. So make sure you have proper cooling and your machine’s ventilation system is up to the task.
In our example, we gradually increased the clock speed from 3.6 GHz on a Core i7 5820K to 4.6 GHz by gradually increasing our multiplier to 46 and our voltage to 2.1. Doing so improved the Cinebench score from 998 to a remarkable 1,317 — a 30% performance boost! Without overclocking, you’d likely need to pay hundreds of dollars to achieve a similar speed increase.
Cinebench CPU test results before overclocking.
Cinebench CPU test results after overclocking.
What happens if I get a black screen when I overclock?
In some cases, your PC won’t boot up after an overclock. Don’t worry — resetting the BIOS reverts all settings to their default values, so you can try the last setting that worked for you. Usually the motherboard has a button that says “Clear CMOS” or “Reset CMOS.”
In the worst case, you can pull out the little battery on your motherboard, wait 10 seconds, and put it back in. Refer to your manual for more instructions.
What is overclocking a CPU?
Overclocking a CPU means increasing the processor’s clock rate — the speed at which the CPU works to perform calculations — above the manufacturer’s specifications. Overclocking works by running a CPU’s clock speed at a higher frequency to execute more operations per second and increase performance.
What does overclocking do, exactly?
Overclocking allows you to run your processor at higher clock speeds than originally intended. This lets you do resource-intensive tasks faster and more smoothly, such as editing videos or photos or gaming. Generally, overclocking makes your computer feel snappier.
The speed of your processor is determined by two factors: clock speed and the CPU core ratio. In technical terms, overclocking boosts the clock speed, increasing the number of cycles your CPU executes per second, measured in GHz (gigahertz). Each cycle generates an electrical pulse, or “clock signal,” that triggers the CPU’s integrated circuits to process data.
In the example above, we went from 3.6 GHz to 4.6 GHz — quite an achievement! So that’s what overclocking does. Besides your CPU, you can also overclock your GPU.
Is overclocking safe?
Overclocking is totally safe, because today’s computers have built-in safeguards to power down or turn off components if they get too hot. While overclocking means pushing your hardware beyond its official limits, with modern materials, your hardware will likely have no problems.
The biggest risk in overclocking your PC is that the temperature of your CPU or other hardware will increase. But even that is rare.
It’s almost impossible to “fry” your CPU by overclocking it or to crash your computer entirely. If the clock is set too high, your PC will simply reboot or bluescreen. As mentioned above, it’s easy to revert to the original settings using the CMOS reset.
But remember that giving the CPU more voltage and higher clock speeds does put additional stress on it. That means that you’ll reduce the CPU’s lifespan a bit. For example, you might reduce the CPU lifespan from 15-20 years to maybe 12-15 years, but it’s hard to say. Regardless, you’ll almost certainly replace your computer before then anyway.
If you’ve built your own gaming rig, make sure your computer’s cooling system can handle overclocking before pushing your hardware beyond its specified limits. For more, check out our article on how to build your own gaming PC.
Can I overclock my CPU?
In theory, any CPU can be overclocked. But overclocking can be done only by raising what’s called the “base clock” — that is, the clock speed of your motherboard and your entire system (including the CPU, RAM, and PCI Express devices, such as sound cards or graphic cards).
But just because you can overclock a CPU doesn’t mean you should. If you push your CPU too far, you may encounter stability issues, because not every processor truly supports overclocking. When it does, the CPU has a so-called unlocked multiplier.
To find out if your processor supports overclocking, examine the name of your CPU. Intel adds the letter “K” to processors that can be overclocked, such as the Intel Core i7 9700K. And all processors from the Intel “X” series (used primarily for professional multimedia) can be overclocked.
As for AMD processors, there’s nothing to worry about. All modern AMD Ryzen CPUs are “unlocked” and can be overclocked. If you have an older model, check your PC specs and run a quick Google search to see if overclocking is possible.
What about Intel overclocking?
Intel processors that end with the letter “K” — for example, Intel Core i7 9700K — can be overclocked. And all processors from the Intel “X” series can be overclocked. But not all Intel CPUs are unlocked and capable of being overclocked.
Can you overclock a laptop?
Overclocking the CPU of a laptop is theoretically possible, but it’s usually not advisable. The internal components of a laptop are packed tightly together, and with much more limited cooling systems compared with desktop computers, overclocked laptops can overheat and cause serious and permanent damage to your machine.
That’s why most laptop CPUs are locked so they cannot be overclocked by raising the clock speed. But if you’re confident you know what you’re doing, unlocked laptop CPUs can be overclocked just like the CPUs of desktop PCs, by raising the base clock rate.
If you’re looking for a safer way to boost your computer’s performance, use an all-encompassing security and optimization tool like Avast One, which will clean up your laptop, give you a VPN, and protect your device from malware.
Why should I overclock my CPU?
If you want more performance for gaming, rendering, coding, or simply for your day-to-day tasks, a higher core clock can help. Overclocking is often a quick, easy, and cost-efficient way to unlock better performance, especially when compared to the cost of upgrading to a new CPU or even a new computer.
Is overclocking your PC worth it?
Overclocking a PC is usually worth it if your computer is older or if the components are outdated. You’ll see greater results from overclocking older PCs, because performance will increase closer to the level of today’s more powerful components. You can overclock newer machines, too, but performance gains may be more limited.
Should I overclock my CPU for gaming?
Overclocking is a good way to boost gaming performance, because it can help increase FPS. While many games are “GPU bound,” meaning that most calculations happen on the graphics card, a significant part of gaming performance also depends on processor performance.
But remember that while an overclock can give you more frames per second in many scenarios, it won’t help much if your OS and its programs aren’t properly optimized. Use a dedicated PC optimization tool to make sure no software or setting is slowing you down.
Optimize your PC the easy way
If you don’t want to risk destabilizing your hardware and just need an additional boost, it’s easier to use automated optimization software. At Avast, we developed a patented technology called Sleep Mode, which detects and disables resource-draining programs when they’re not being actively used.
To get the maximum FPS out of your system, put your unnecessary apps and processes to sleep. Download a free trial of Avast Cleanup, then go into the Speed Up section and look for Background and Startup Programs.
How to setup your computer to auto Power On after power outage.
In this tutorial I will show you how you can setup your computer in order to automatically power on after power outage. This guide can be very helpful for people that want to connect to their computer and work remotely (from a distance) when they are on a different location.
How to automatically start on (turning computer back / power on) after power outage.
Step 1. Modify Power settings inside your BIOS.
Power On your computer and press DEL or F1 or F2 or F10 to enter BIOS (CMOS) setup utility. (The way to enter into BIOS Settings depends on the computer manufacturer).
Inside BIOS menu, look under the following menus to find for a setting named “Restore on AC/Power Loss” or “AC Power Recovery” or After Power Loss.
“Advanced” or “ACPI” or Power Management Setup.
Note: The “Restore on AC/Power Loss” setting can be found under different places inside BIOS setup according to computer manufacturer.
Set the “Restore on AC/Power Loss” setting to “Power On”.
Save and exit from BIOS settings.
Step 2. Modify Windows to startup normally after power corruption,
In Windows 7 Vista OS, after power failure Windows launches by default the “Startup Repair” settings instead of starting normally. But in repair mode, you can not control your PC unless you sit in front of it. To bypass this situation and to force Windows to start in normal mode after power outages or improperly shutdown, do the following:
Open an elevated command prompt window by going to:
In the command window, type the following command and press Enter.
After pressing the “Enter” key, Windows should return an “Operation completed successfully” message.
Close command prompt window and you ‘re done!
Attention: Always use a UPS (Uninterruptible power supply) to protect your computer hardware from voltage outages and voltage strikes. Power outages can cause serious problems on your hardware like PSU (Power Supply Unit) destruction or HDD (Hard disk) destruction (data loss).