How to Turn on iPhone Background
Find out how privacy settings and location services help protect your privacy on iPhone, iPad, and iPod touch.
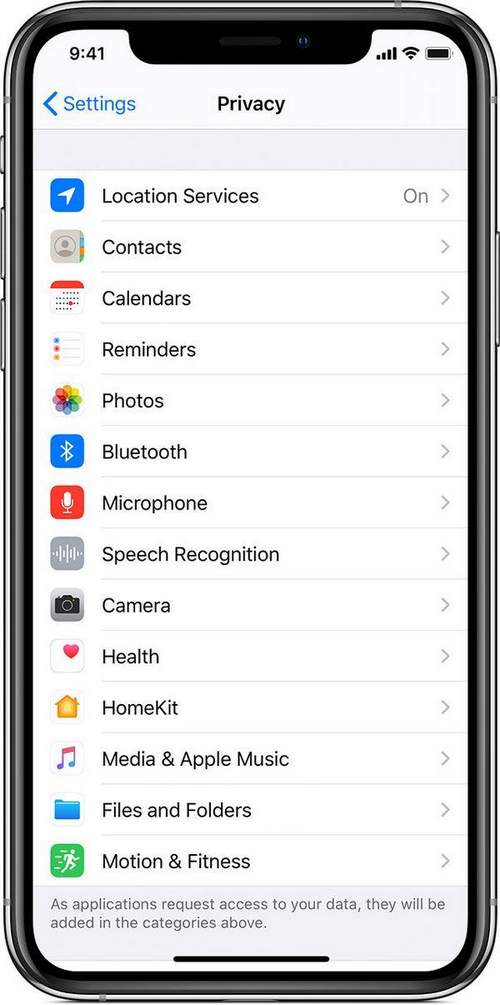
Privacy settings
Privacy settings in iOS and iPadOS allow you to control the access of applications to the information stored on the device. For example, you can allow the social network application to use the camera so that you can take pictures and send them using this application. You can also allow access to your contacts, while the messaging application can find friends who are already using this application.
- geolocation services
- contacts,
- calendars
- reminders
- a photo,
- Bluetooth
- microphone,
- speech recognition,
- camera
- health,
- HomeKit,
- Media and Apple Music
- study,
- Files and folders
- movement and fitness.
On your device, in this list you can select the data type to find out which applications requested permission to use them. The application will not appear in the list until it asks for permission to use your data. You can add or remove permission for any application that requested access to data. If you give an application access to a specific data type, it can only access that type of data.
If you sign in to iCloud, apps by default access iCloud Drive. You can also view the list of applications that are allowed to use iCloud and manage them in the Settings menu iCloud
If you allow third-party applications or websites to use your data or current data about your location, you are subject to their terms of use, privacy policies and rules. To learn how certain apps and websites use location data and other information, review their terms, privacy policies, and policies. Information collected by Apple is processed in accordance with Apple’s privacy policy.
Using device geolocation services
With your permission, geolocation services allow applications and websites (including Maps, Camera, Weather, and others) to use data from cellular network 1, Wi-Fi 2, GPS 3, and Bluetooth 4 to roughly determine your location 5.
In applications that use this data, such as Maps, your current (approximate) location is marked with a blue marker. If your location cannot be accurately determined in the Maps application, then you will see a blue circle around the marker. The radius of the circle depends on the accuracy of the determination. the smaller it is, the higher the accuracy. When geolocation services are activated, a black or white arrow appears in the status bar.
The availability of maps and routes, as well as the correct operation of applications that use location data, depends on data services. These services are subject to change and are not available in all areas. In this regard, maps, routes or location information may be inaccurate, incomplete or even absent. To clarify the information, compare the data displayed on the screen of the device with the environment surrounding you and navigate along the road signs.
Request permission to use your location data
The first time you try to get data about your location, the application will ask for permission. You’ll see information about the application that is requesting access to your geo-location, as well as the reason why such access is required.
Some applications require access to the geolocation only when using them. An application is considered “used” if you are working with it in active mode or if it uses geolocation data in the background. In the second case, a blue indicator will be displayed in the status bar.
If you have granted the application “Using” permission, it may request permission to use data about your geo-location when working in the background.
If you allow the application to use your location information in the background, your device will occasionally remind you that the application uses your location information and display this information on the map. You will also be asked if you still want to allow the application to use your location information when running in the background.
In iOS 13 and iPadOS 13, you can click “Allow once” so that the application gets access to geo-location data only with one session (once). If you close the application, and then run it again, and it again tries to access the data about your location, the request will be displayed again. Applications will not use your location information until they request (and receive) your permission.
You can change your mind at any time and update your settings in the “Settings” “Privacy” menu “Geolocation Services.” You can enable geolocation services when you first configure your device in the Setup Assistant application, or at any time using the Geolocation Services option. Access to geolocation services data can be configured individually for each application and system service. If geolocation services are turned off, applications cannot use data about your geolocation, regardless of whether they are active or in the background. This will limit the capabilities of many Apple and third-party applications.
If you want to reset all geolocation settings to factory defaults, go to the Settings menu “Basic” “Reset” and click “Reset Geo-Settings”. After resetting your geolocation and privacy settings, apps will stop using your location data until you give them permission to do so.
“Settings” “Confidentiality” “Geolocation Services.”
“Settings” “Confidentiality” “Geolocation Services” “System Services”.